Waste Management and Recycling
HIWIN is dedicated to the prevention, reduction, and reuse of waste, and fully promotes the goals of a circular economy throughout procurement, product design, and manufacturing. To raise awareness of waste management, HIWIN arranges waste management training for employees to help them stay informed about future trends. In 2024, a total of 473 participants attended, with approximately 261 training hours. In addition, by holding regular waste project meetings and continuously promoting the ISO 14001:2015 environmental management system, HIWIN reviews source reduction and improvement strategies, formulates waste reduction plans, and actively moves toward the goal of zero waste.

HIWIN handles both general and hazardous business waste and follows a waste management procedure-based control system. To achieve the goal of zero landfill, the Company has increased investment in waste classification, resource recycling, and circular reuse, while continuously optimizing internal processes and technologies. HIWIN plans to reduce landfill volume each year and explore innovative technologies or external treatment partners for waste types that are difficult to reuse, gradually working toward the reduction of landfill. At the same time, the Company has set long-term goals to strengthen recycling and reuse, enabling effective waste management and ongoing waste reduction to facilitate resource reuse. By implementing the five major principles of waste management, HIWIN aims to minimize waste production, lower carbon emissions, and lay a solid foundation for achieving zero waste and zero landfill.
Waste Resources
In 2024, HIWIN generated a total of 10,422t of waste-of which 10,163t were general industrial waste and 259t were hazardous industrial waste. The waste generated was handled through reuse and direct treatment (incineration and landfill). Specifically, 8,847t of general industrial waste were treated for reuse, representing 85% of total waste generated. Due to reductions in raw material residues, sludge mixtures and hazardous industrial waste, the reuse rate rose by 4% compared with 2023.
The intensity of general industrial waste in 2024 increased by 0.02t/ NT$ million compared to 2023, while the total volume rose by 4%. Waste-reduction efforts will continue into 2025. In contrast, the intensity of hazardous industrial waste in 2024 decreased by 0.02t per NT$ million compared to 2023. Since the hazardous-waste acid-liquid treatment equipment was completed in May 2024 and optimization is ongoing, total hazardous industrial waste volume declined by 45.5%.
Source Reduction Measures
At HIWIN, waste management adheres to the principles of recycling and reusing. We regularly conduct life cycle assessments for various stages, including raw materials, products, shipping, packaging, etc., to prevent ineffective waste treatment caused by environmental impacts.
Circular Economy Promoting
Waste Vendor Audits and Guidance
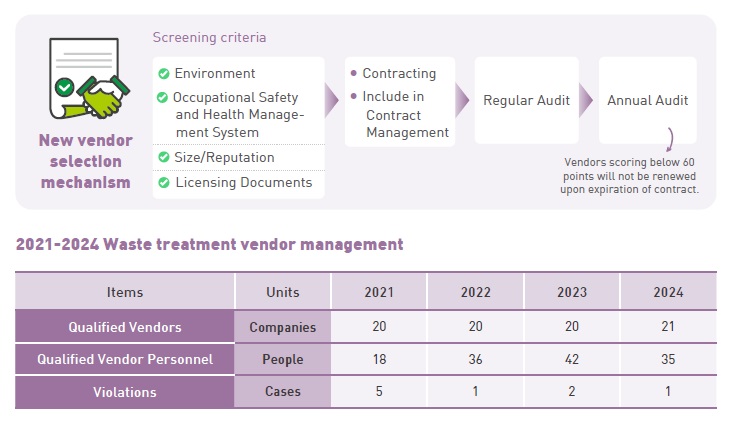
HIWIN’s operational waste has all been outsourced for disposal to government-approved vendors selected by the company’s Environmental Protection Department and Purchasing Department, based on six key screening criteria. After contract signing, these vendors handle outsourced waste collection, processing, and flow management. Only vendors scoring 60 points or above in the evaluation are included on the qualified vendor list. In 2024, HIWIN had a total of 21 qualified waste vendors, all rated as excellent in on-site evaluations.
In 2024, all waste collection personnel from HIWIN’s qualified vendors received in-house contractor training for entry into HIWIN facilities. Waste disposal is reported in accordance with the Ministry of Environment regulations. An internal audit system is in place: each department collects and sorts waste by category and transports it to designated storage areas, where dedicated personnel notify qualified waste removal vendors to enter the facility for waste clearance.

Waste removal audit